THE DANGER OF PLANNED OBSOLESCENCE Planned obsolescence is a phenomenon observed across technological industries, referring to the practice of designing…
Since 3D construction printing first emerged in the 2010s, it has grabbed huge attention as it could be a new revolution…
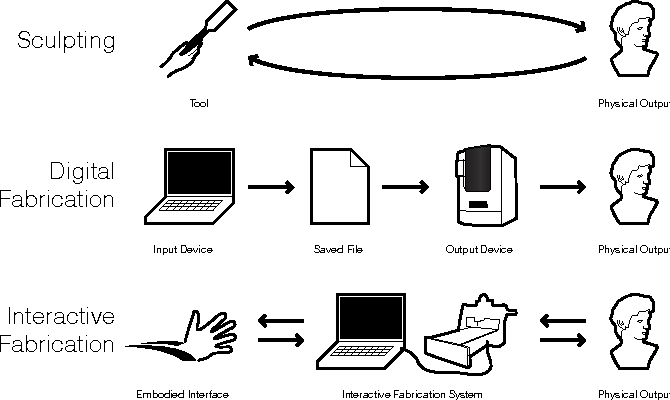
How interfaces expand and contract possibilities Via lines of code, numerical points in space and all the edges inbetween, the…
For my research, I scrubbed the internet for the most obscure and bizarre 3d printers I could find. In this…
What is 3d printed textile? 3D printed textile refers to the process of using additive manufacturing techniques to create fabric-like…
Oh yeah! This is my research.
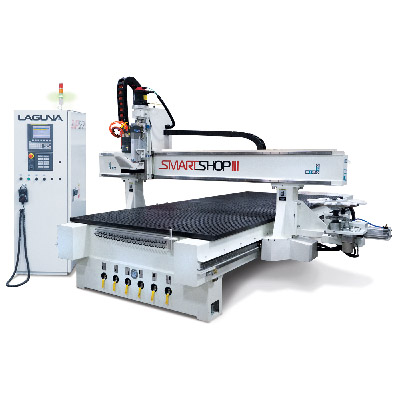
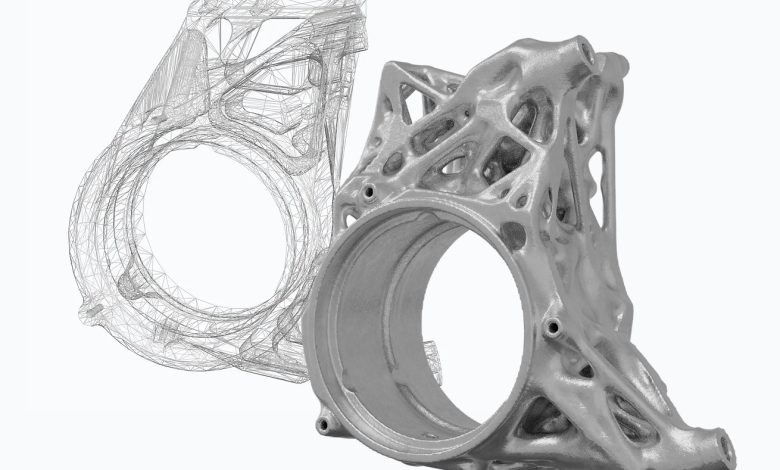
Design for Additive Manufacturing is a process in which base design work is created specifically for the possibilities and limitations of additive manufacturing, or 3D printing. This differs from traditional design practices, as many of the ways in which CAD manufacturing is done today are drawn from pre-digital workflows. Additive manufacturing allows for the creation of structures that would otherwise have been made of many separate parts or have been simply impossible.
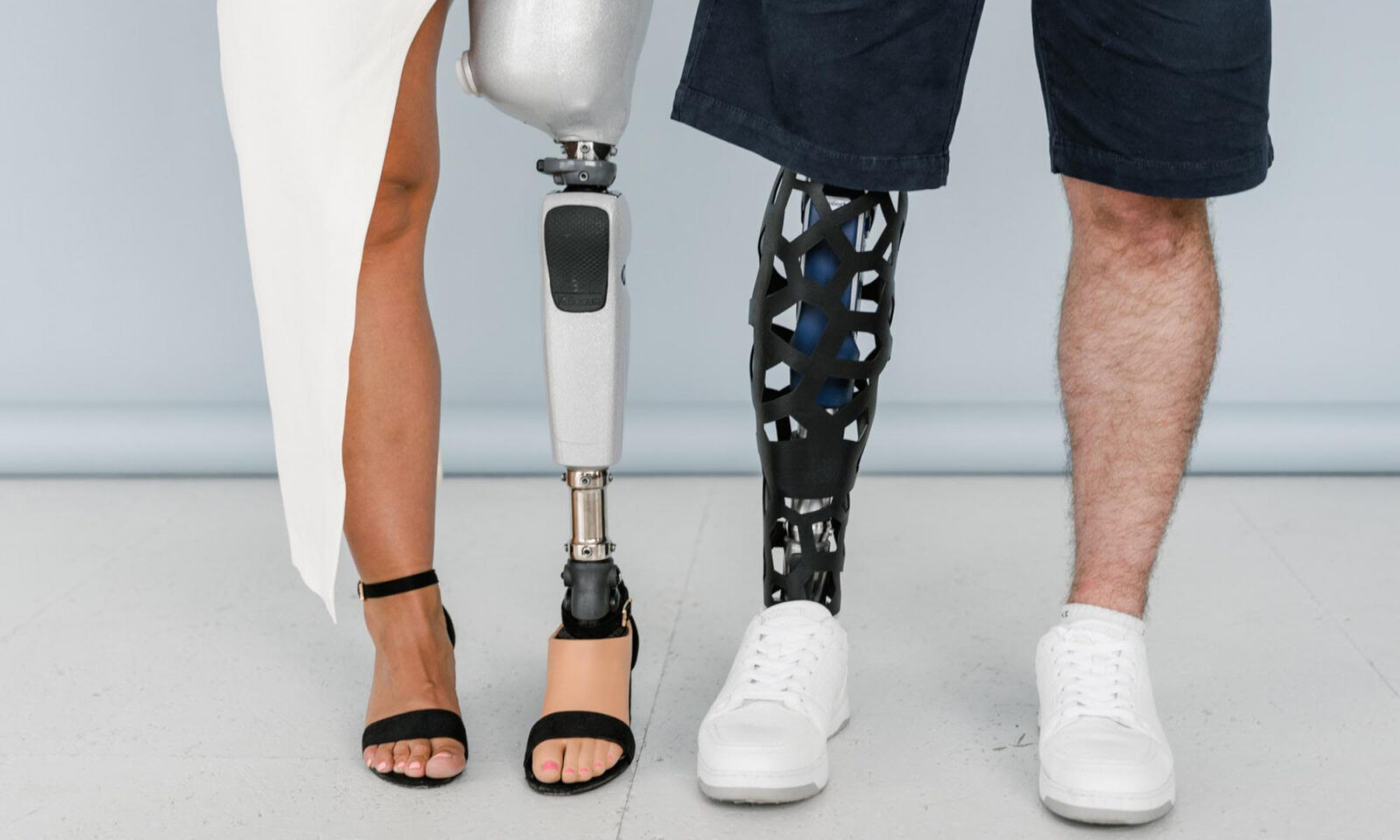
The prosthetic industry has been around for a long time, but recent innovations in technology are changing the way that prosthetics and orthotics are produced. A prosthetic is a device that “replaces missing body parts or limbs,” while an orthotic “stabilizes, supports, immobilizes, or relieves part of a body or limb, or corrects defective positions.” Both of these consist of functional parts, or joints, and areas that connect with the patient’s body. Due to the level of manual work involved in creating these devices, it is nearly impossible to replicate outcomes. Digital fabrication, however, can eliminate these “unwanted deviations” as it standardizes the process, as well as allows for cost reduction and improved aesthetics.
FA stands out through its commitment to deploying cutting-edge techniques across diverse fields. Nour Abuzaid, a key figure within FA, emphatically asserts that technology is not neutral but shaped by specific political and historical contexts. The agency’s primary objective is to investigate global human rights violations, employing a multidisciplinary team and a variety of methodologies such as geolocation, 3D modeling, audio analysis, data mining, fluid dynamics simulation, and virtual reality.
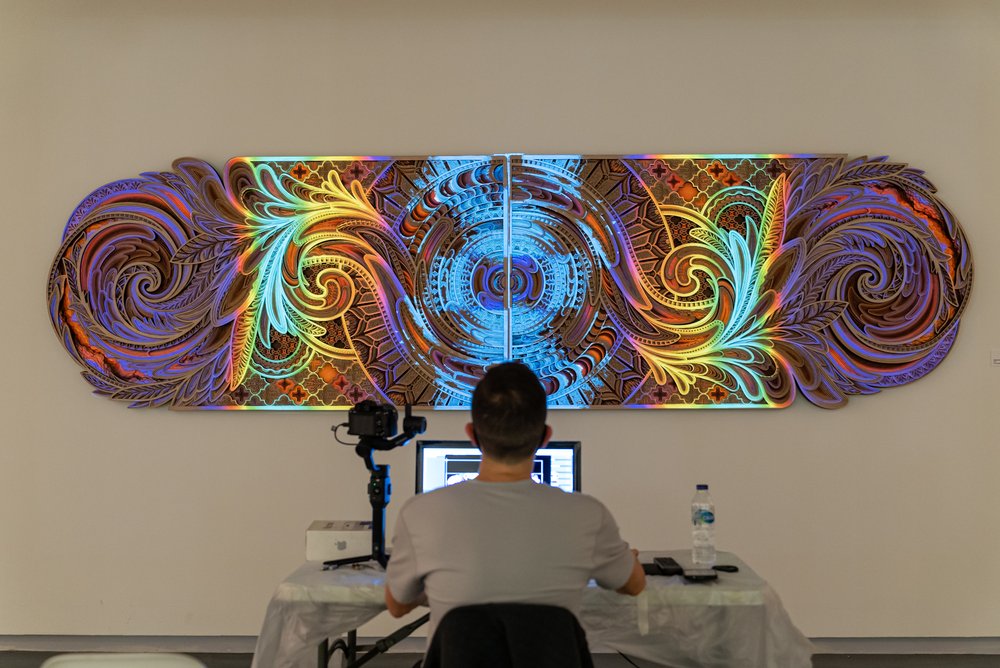
This research explores the captivating world of multilayered wall art, focusing on how the incorporation of multiple layers enhances the…